In Silverlight and WPF, when working with UserControls and Behaviors, you may find yourself in situations where you need to call a method or access a property that is stored in the parent. This parent can be anything - it could be a container or it could be another UserControl. Accessing what you want in those locations is not as straightforward as you may imagine it to be.
To describe this scenario a bit more, let's look at the following diagram where I am simplifying to a world where the parents and children are just Window, UserControl, or Behavior types:
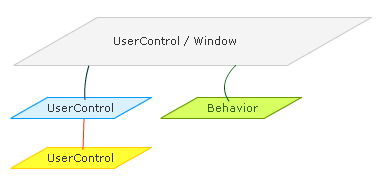
In this short tutorial, I will describe a few things:
-
How to access the contents of your application's root Page or Window regardless of where you are.
-
How to access the contents of a parent user control such as the Yellow user control calling something in the Blue user control.
-
How Behaviors are a bit different.
The syntax for both WPF and Silverlight can be a little different, so if there are any differences, I will provide both versions for the scenarios I list above.
Accessing the Root
The most common type of cross-usercontrol communication you would engage in is one where you are trying access the root of your application. The root of your application in Silverlight is of type UserControl, and the root of your application in WPF is of type Window. This distinction is important because it results in a varying syntax.
The syntax for accessing the root UserControl in Silverlight is:
- UserControl rootPage = Application.Current.RootVisual as UserControl;
The syntax for accessing the root Window in WPF is:
- Window rootWindow = Application.Current.MainWindow as Window;
The above code will hook into your root and provide you with access to any types that are available to UserControl and Window.
So now, you get access to the root element, but you probably don't want this particular approach. The problem is that casting to both UserControl and Window is very generic, and it contains no references to anything you may have done. Any elements you added in XAML or any properties and methods you added in your code-behind file are hidden from view.
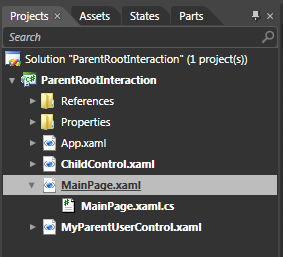
The reason is actually pretty simple. The root of your application is not actually UserControl or Window. It is something derived directly from UserControl or Window. To fix this, you need to cast the returned value to the actual type of your root element. By default, in Expression Blend, the type of your root usercontrol is MainPage in Silverlight:
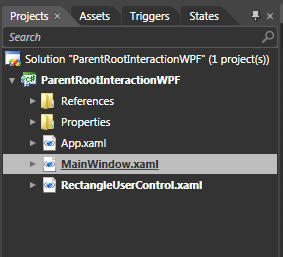
In WPF, the type of your root window is MainWindow:
This means, you will need to make just some minor tweaks to your code. For Silverlight, your code now becomes:
- MainPage rootPage = Application.Current.RootVisual as MainPage;
For WPF, your code is:
- MainWindow rootWindow = Application.Current.MainWindow as MainWindow;
While MainPage and MainWindow are new types, they are directly derived from UserControl and Window respectively. This means that any properties or methods you would expect to see either in UserControl or Window are still accessible to you. In your own projects, if you are not using Expression Blend, be sure to set the type of the root element appropriately because you cannot assume that MainWindow and MainPage will actually exist.